Table of Contents
Introduction
Diodes are semiconductor devices. Semiconductor devices are those types of devices that can conduct electricity between conductors and insulators. Diodes are the most popular semiconductor devices used in electronics. Diodes are made up of two types of semiconductor material mainly Silicon and Germanium. Now, let’s dive into the world of diodes and their applications.
What is a diode?
A diode is a semiconductor device that flows voltage and current in one direction only. It comprises two junctions, mainly positive(p) and negative(n). Both p and n junctions are sandwiched together to form a p-n junction diode. The voltage drop of the silicon semiconductor diode is 0.7V, whereas the voltage drop of the germanium diode is 0.3V. The most commonly used semiconductor diode is the silicon diode.
Symbol of diode
The positive side of the diode is called the Anode and the negative side of the diode is called the Cathode
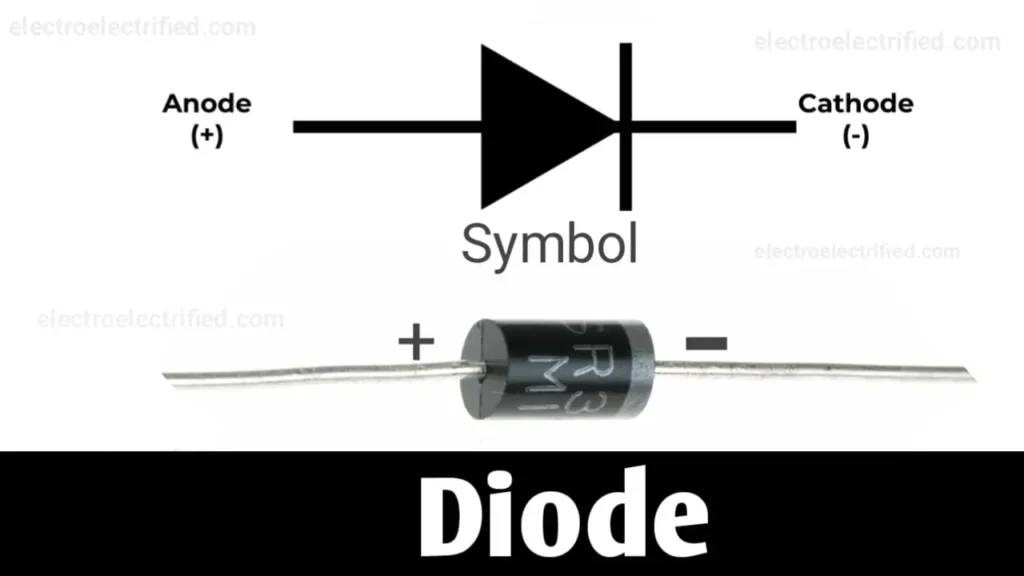
How does a diode work?
The diode works similarly to the check valve of the water pipe. When water is flowing randomly through the pipe then we place the check valve between the pipe which is used to flow water in one direction. Similarly, we use the diode in electronic circuits to only flow voltage and current in one direction.
Diode works in two biases namely Forward bias and Reverse bias.
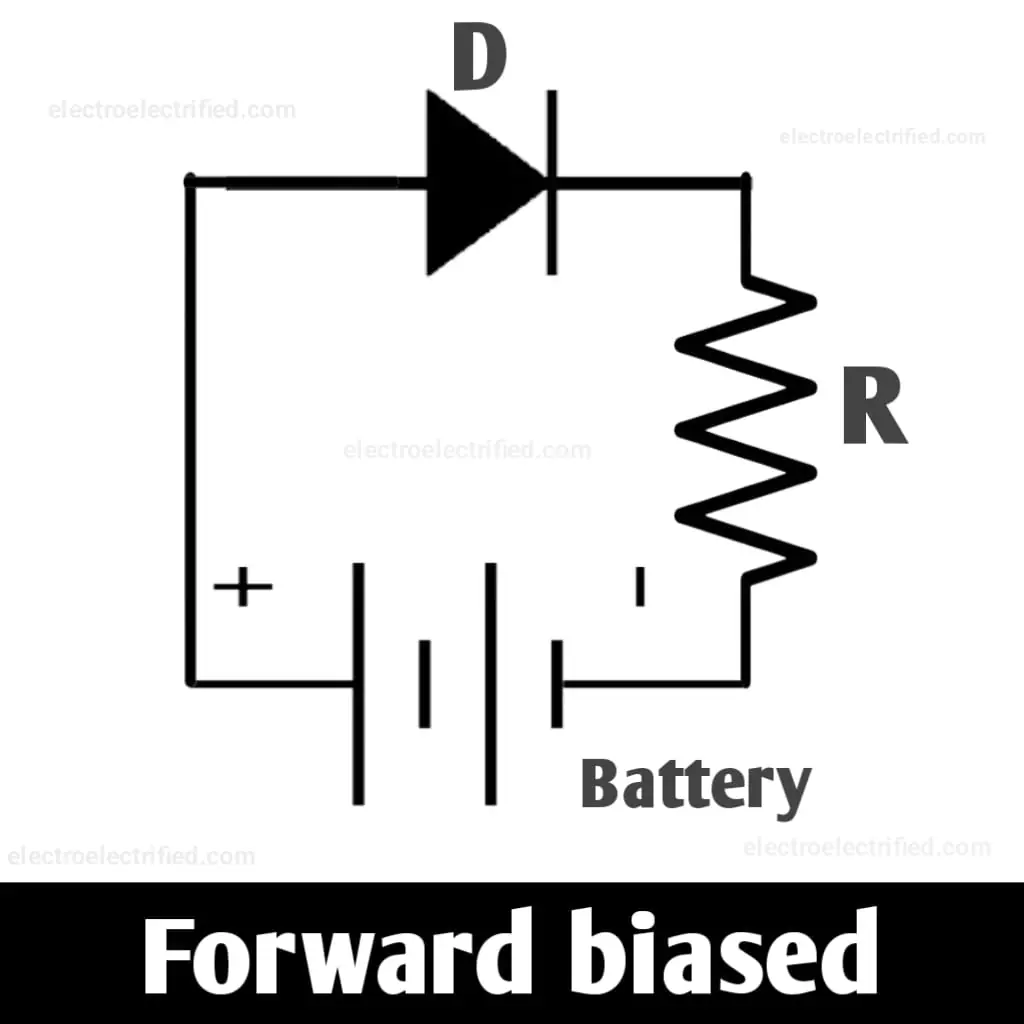
Forward bias
When we connect the positive terminal of the diode with the positive terminal of the battery and the negative terminal of the diode with the negative terminal of the battery, the diode is said to be forward-biased.
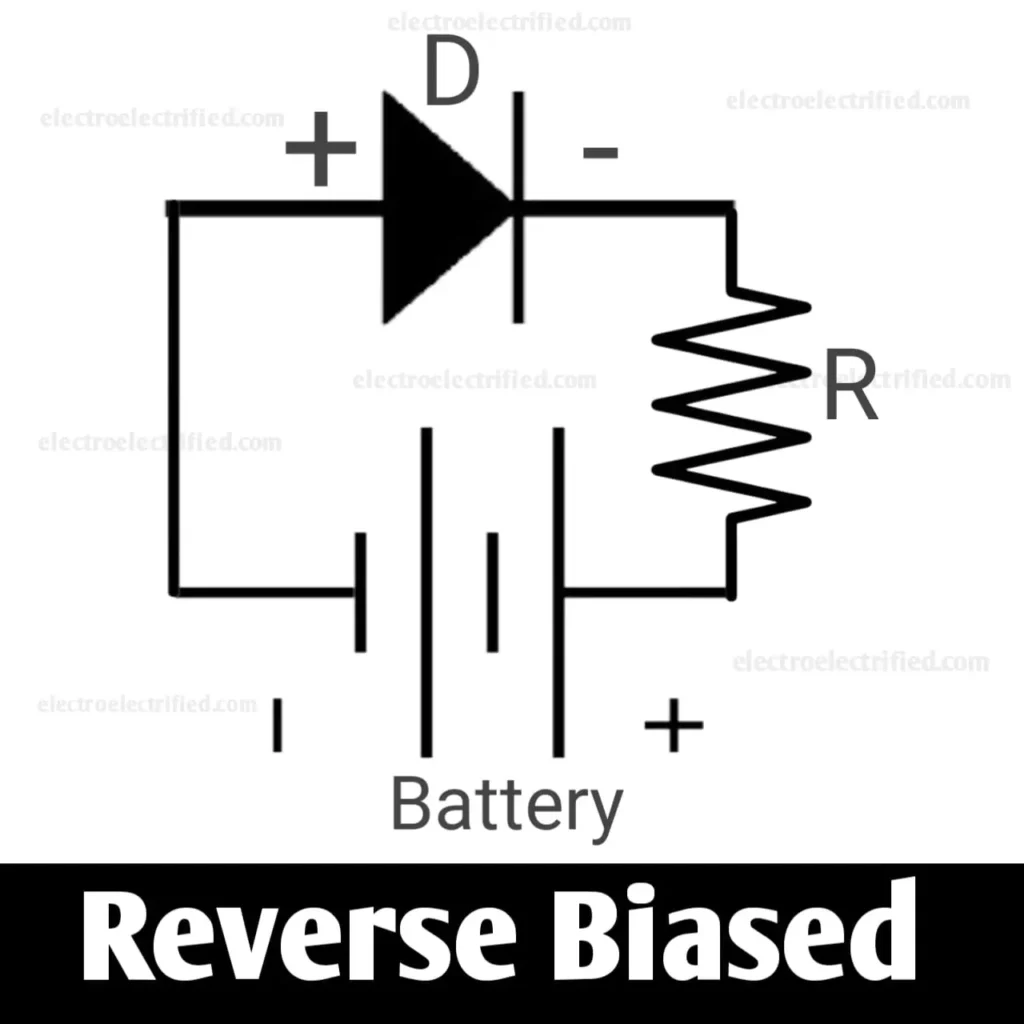
Reverse bias
When we connect the positive terminal of the diode with the negative terminal of the battery and the negative terminal of the diode with the positive terminal of the battery, the diode is said to be reverse-biased.
Types of diodes
- PN junction diode
- Schottky diode
- Light Emitting Diode
- Avalanche diode
- Zener diode
- Laser diode
- Photodiode
- Gunn diodes
PN junction diode
- PN Junction diode is a fundamental diode made from the joining of two n-type and p-type semiconductor materials.
- The p-type semiconductor material is formed when the silicon is doped with a small amount of Boron.
- The n-type semiconductor material is formed when the silicon is doped with a small amount of Antimony.
- The junction potential of a silicon diode is 0.7 volts.
Schottky diode
- Schottky diode is a fast recovery diode made by the junction of semiconductor material with metal.
- Schottky diodes have low turn-on voltage, fast recovery time and low-loss energy at higher frequencies.
- It has a swift switching action.
Light Emitting Diode (LED)
- LED is a semiconductor component that emits light when electric current is passed through its two terminals.
- LED is a two-terminal device.
- The colour of light depends upon the energy, the electrons are required to cross the band gap of semiconductor material to glow the LED.
Avalanche diode
- Avalanche diodes are those types of diodes that are designed to disconnect the circuit at some specific voltage.
- These diodes control system pressure and guard electrical systems from surplus voltages.
- While selecting these diodes, one must consider their breakdown voltage, power rating and temperature range.
Zener diode
- Zener diode is a type of pn-junction diode that works in reverse-biased regions.
- It is a type of voltage regulator that limits current to a certain level, per the configuration of the Zener diode.
- It works in both regions whether it is forward-biased or reverse-biased. But it is designed for working in reversed-biased regions.
- For a Zener diode to work in the breakdown region, the positive terminal(Anode) is connected to the negative terminal of the battery and the negative terminal(Cathode) is connected to the battery’s positive terminal.
Laser diode
- As a semiconductor, a laser diode uses a p-n junction to produce coherent radiation, either in the visible or infrared spectrum, with the same frequency and phase.
- The technology used in making of laser diode is similar to LED’s.
Photodiode
- Photodiodes are diodes that use light energy and convert it into electrical energy.
- Photodiodes are also called as light detectors, photo sensors and photo sensors.
- Photodiodes work in reverse-biased conditions. When light falls on the surface of the photodiode it consumes light energy and converts it into electric current.
Gunn diodes
- Gunn diode is a type of passive semiconductor diode which have negative differential resistance.
- It is only an n-doped semiconductor diode.
- Gunn diodes are used in high-frequency electronics.
Diodes and their applications
- Rectifier
- Signal limiters
- Voltage regulators
- Switches
- Signal modulators
- Signal mixers
- Signal demodulators
- Oscillators
Rectifier
The rectifier is an electronic device that converts alternating current(AC) into direct current(DC). In a rectifier circuit, the diode plays a very important role in converting oscillating AC into direct current.
Rectifier are of 3 types:
- Half-wave rectifier
- Full-wave rectifier
- Bridge rectifier
Half-wave rectifier
Half-wave are the types of rectifiers that use only one diode for the conversion of AC to DC. It passes only one-half cycle of AC waveform and blocks another cycle of AC waveform.
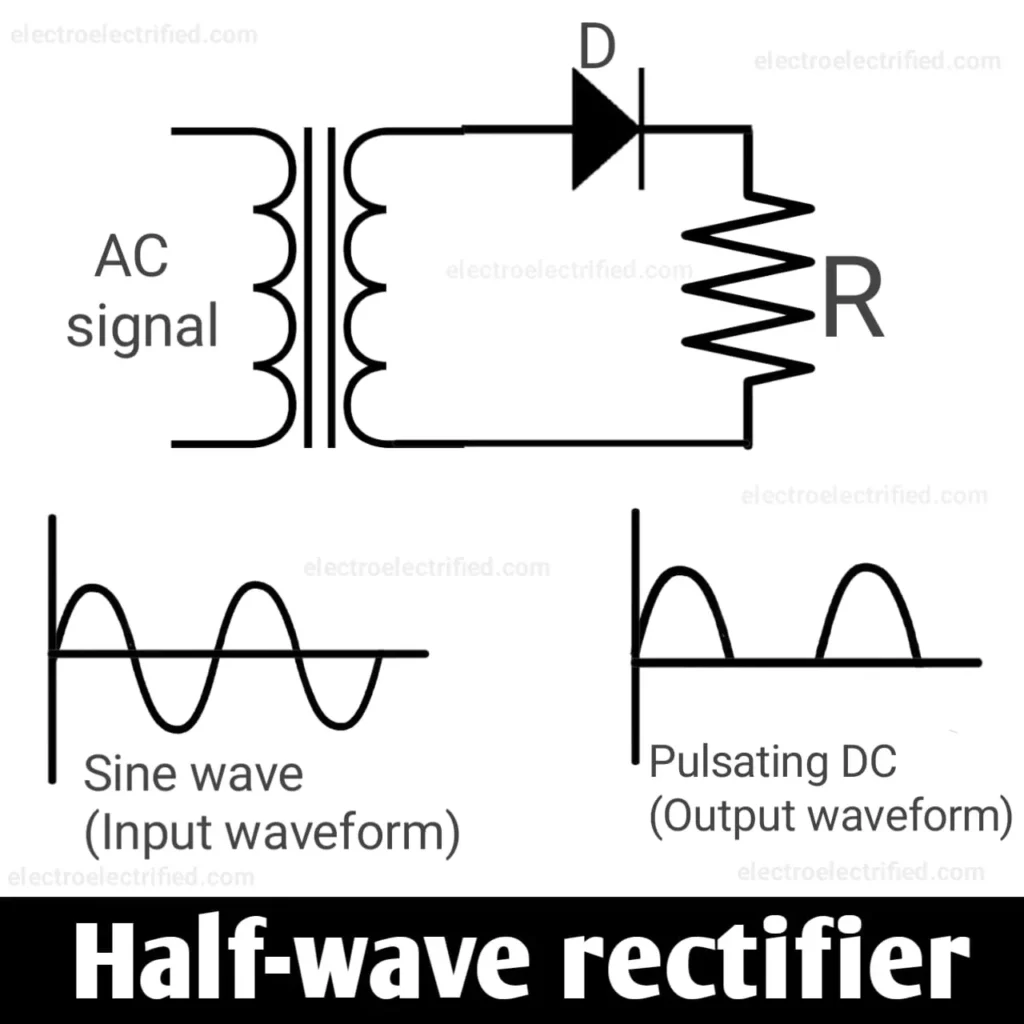
In the above diagram, the AC passes from the step-down transformer to the diode (D) and then to the load connected (R). In the first half-cycle, the current flows from the diode(D) to load but in another half-cycle current doesn’t flow which results in pulsating DC output.
Full-wave rectifier
In a full-wave rectifier, two diodes are used to convert AC to DC. It uses a centre-tapped transformer to convert the AC waveform into a constant pulsating DC waveform.
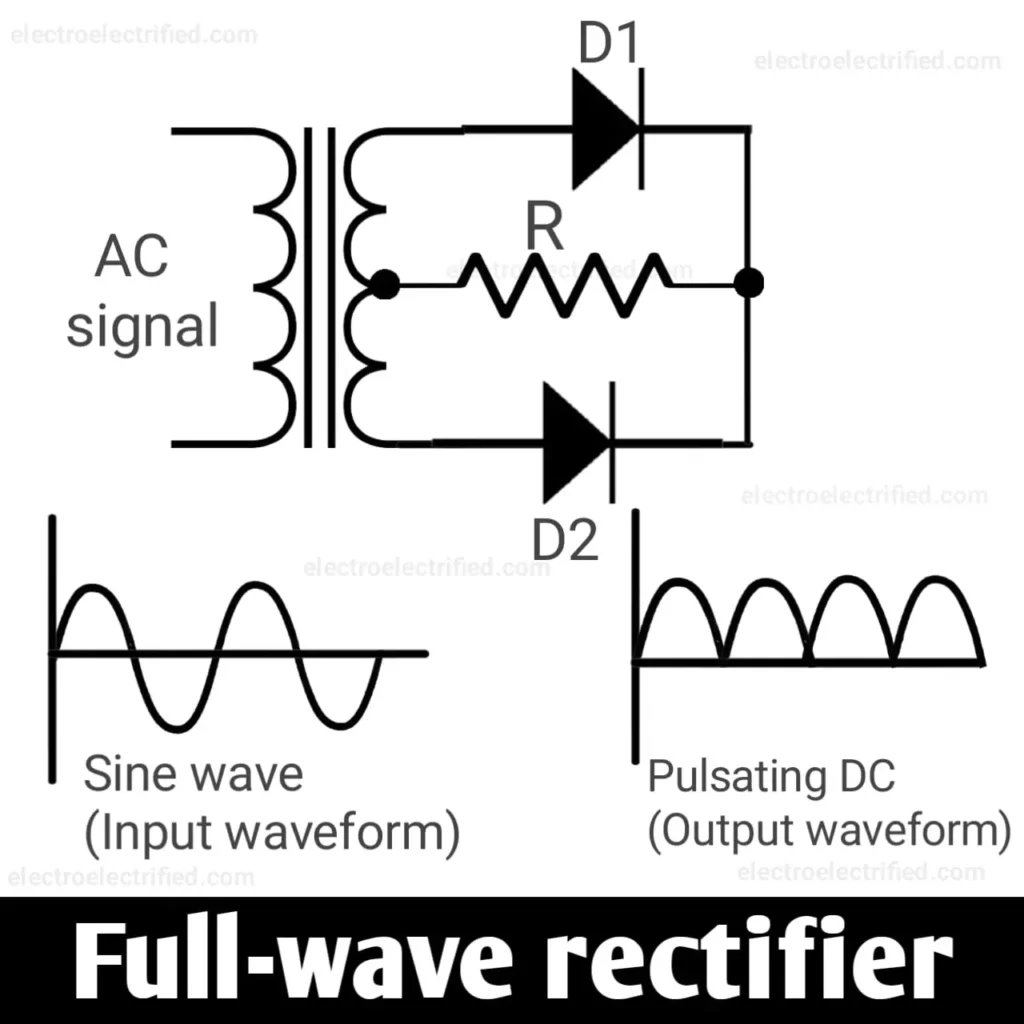
In the above diagram, for the first half-cycle AC passes from the diode (D1) and then to the resistor (R) and then goes back to the transformer from centre-tapped winding. In the second half-cycle AC passes from the diode (D2) and then to the resistor (R) and then goes back to the transformer from centre-tapped winding. This process keeps on repeating and thus, we get a DC pulsating continuous output waveform.
Bridge rectifier
In the bridge rectifier, four diodes are used to convert AC to DC. As in this rectifier configuration, four diodes are used so the voltage drop is high.
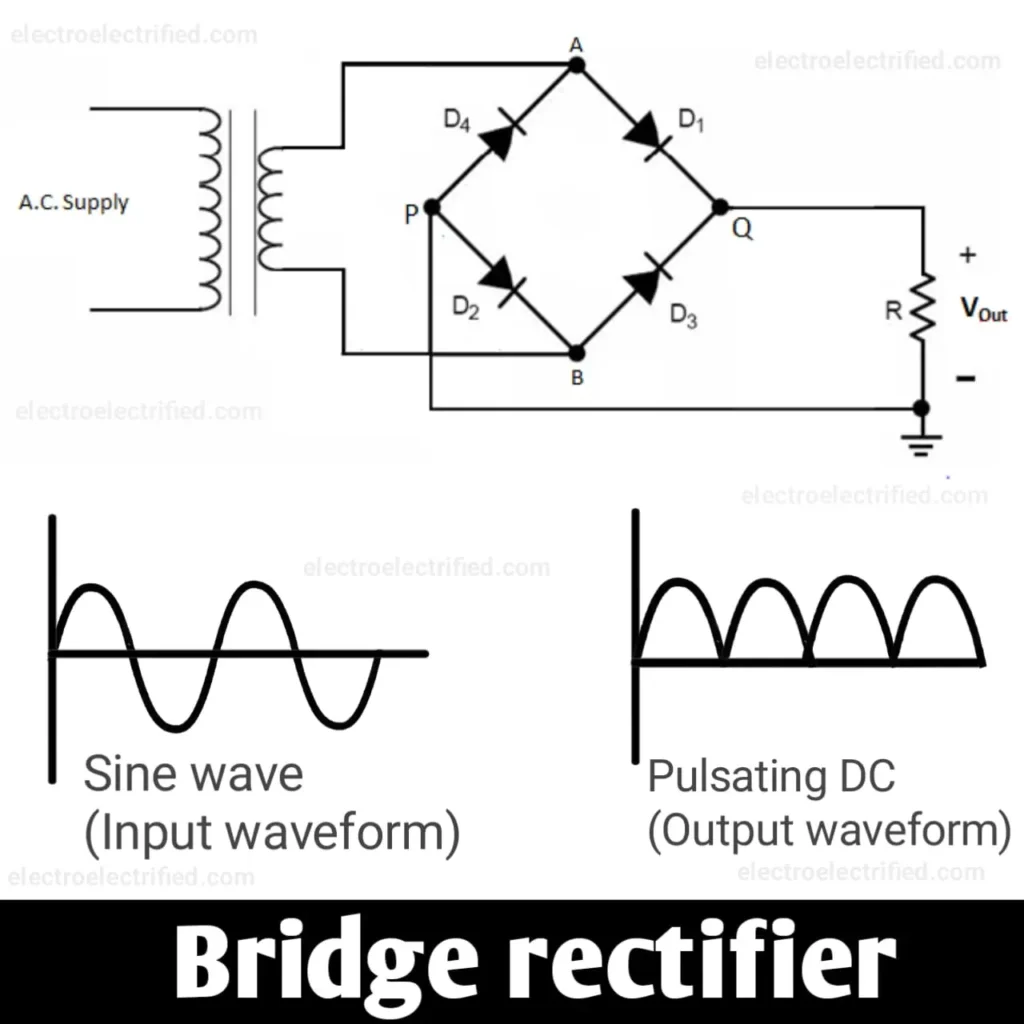
In the above diagram, the first half-cycle diode D1 and D2 work and another half-cycle diode D3 and D4 work. From the Diode D1 and D3, positive (+) potential is obtained whereas from the diode terminal D2 and D4, negative (-) potential is obtained.
Frequently asked questions
Ques 1: Is diode unidirectional or bidirectional?
The diode is a unidirectional electronic component that passes current only in one direction (from Anode to Cathode). It blocks current in the opposite direction.
Ques 2: Diode works on AC or DC?
The diode flows current in one direction only. So, it works on DC. If the diode works on AC it passes current only for half-cycle. Thus, the diode converts AC to DC.
Ques 3: What is the voltage drop in the diode?
Voltage drop in the diode refers to the small loss of current while the diode is conducting current in forward-biased. The voltage drop for the silicon diode is 0.7V while the voltage drop in the Germanium diode is 0.3V.
Ques 4: What is inside a diode?
Inside the diode, there are two electrodes called as Anode and Cathode. The Anode is the positive terminal of the diode whereas Cathode is the negative terminal of the diode.
