Table of Contents

Introduction
Welcome to our in-depth guide on resistors, the fundamental components of electronic circuits. If you’ve ever wondered how electronic devices function, resistors play a crucial role in controlling and regulating the flow of electric current. In this comprehensive article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about resistors, including their types, functions, and various applications. So, let’s dive into the essential component that powers much of our modern technology!
What are Resistors?
Resistors are passive electrical components designed to limit or resist the flow of electric current in a circuit. They are made of materials with specific electrical resistance properties, typically measured in ohms (Ω). The resistance value determines how much the resistor impedes the flow of current. Higher resistance means less current flow, while lower resistance allows more current to pass.
What does a resistor do?
A resistor is an electronic component that restricts the flow of electric current within a circuit, helping to control voltage levels and protect other components from damage. Additionally, resistors can be used to adjust signal levels, divide voltages, and provide stability in various electrical and electronic applications.
Types of Resistors
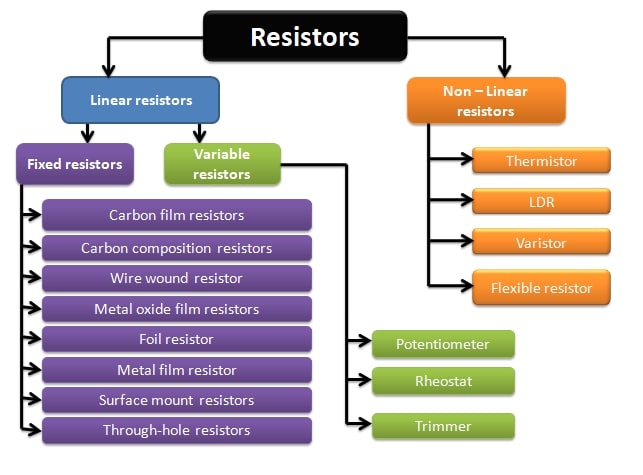
There are two types of resistors commonly used:
- Linear resistors: These resistors follow Ohm’s law. Ohm’s law states that, at a constant temperature voltage is directly proportional to the current flowing through the circuit.
- Non-Linear resistors: These resistors don’t follow Ohm’s law. Their resistance value depends on temperature, light and other factors.
Linear resistors
Linear resistors are further divided into fixed resistors and variable resistors.
- Fixed resistors: These are those types of resistors whose resistance value is fixed by the manufacturer. Its resistance value cannot be increased or decreased. For example: if a resistor is 12ohm it remains 12ohm only its resistance value cannot be changed.
- Variable resistors: These are those resistors whose resistance value can be changed as needed. These are 3-pin resistors, the first pin is left, the second is middle, and the third is right. If we rotate its shaft using a screwdriver its resistance value changes. They are useful in applications where precise resistance adjustments are necessary, like volume controls in audio devices.
Fixed resistors are further divided into the following types:
- Carbon film resistors
- Carbon composition resistors
- Wire wound resistor
- Metal oxide film resistors
- Foil resistor
- Metal film resistor
- Surface mount resistors
- Through-hole resistors
Carbon film resistor
Carbon film resistors are a type of fixed resistor. These resistors are made up of ceramic carriers and have a thin carbon film around them. The carbon film is a resistive material that blocks some current around it. The power ratings of carbon film resistors are around 0.125W to 5W at 70 degrees Celsius.
Carbon composition resistors
Carbon composition resistors are made from cylindrical bodies of powdered carbon or graphite combined with a binder, like clay or resin. The binder serves as an insulator and the carbon powder as a conductor.
Wire wound resistor
An electrical passive component that controls or limits current flow in a circuit is called a wire-wound resistor. A conductive wire is used in the construction of wire-wound resistors. After that, a non-conductive core is encircled by the conductive wire.
Metal oxide film resistors
They are composed of a ceramic rod that has been thinly covered with metal oxides, such as tin oxide. The amount of antimony oxide applied to the tin oxide determines the metal oxide film’s resistance.
Foil resistor
These are high-precision resistors. A very thin piece of resistor is used to oppose the current flowing through it.
Metal film resistor
A metal film resistor is most commonly used in electronics. These resistors are consistent and accurate as compared to other types of resistors. In a metal film resistor, the metal oxide film is deposited on the ceramic core surface. These resistors have better performance and are more reliable.
Surface mount resistors (SMD)
These are rectangular-shaped resistors having silver conductive edges. It is small in size and saves space on PCB (Printed Circuit Board). In the upper part of the resistors, the resistance value code is printed on it. These types of resistors are highly used in mobile devices.
Through-hole resistors
Through-hole resistors are used to reduce the flow of electric current. It comes in 3 variations:
- axial: which leads are at the ends.
- radial: its leads pointing downwards.
- pluggable: terminals plugged into PCB.
Variable resistors are further divided into:
- Potentiometer
- Rheostat
- Trimmer
Potentiometer
A potentiometer is a 3-terminal device used as a voltage divider. The two ends of the potentiometer are connected to opposite ends of the resistive element. The third terminal (middle) is connected to the sliding contact, it is called the wiper. The potentiometer is mostly used for volume controls.
Rheostat
Rheostat is a device that is used to control the current by varying the resistance using the sliding contact. It is a type of variable resistor that is mostly used in electrical circuits. It has no polarity, which means that you can connect it anyway. It is also called a wire wound resistor. Its resistance depends on the length of the resistive track.
Trimmer
The trimmer is the device that is used to manually fine-tune the resistance in a circuit. It is a three-pin device. The two end pins are connected with the resistive element and the third pin ( middle ) is the sliding contact called a wiper. When the wiper of the trimmer is rotated using the screwdriver the resistance increases or decreases, which controls the flow of current in the circuit. The trimmer is mostly used for adjusting the brightness or frequency in radios.
Non-linear resistors
Non-linear resistors are further divided into the following types:
- Thermistor
- LDR( Light Dependent Resistors)
- Varistor
- Flexible resistor
Thermistor
It is a type of non-linear resistor because it does not follow Ohm’s law. Its resistance depends upon the temperature. It is of two types :
- NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient): The higher the temperature, the lesser the resistance.
- PTC ( Positive Temperature Coefficient): The higher the temperature greater the resistance.
Thermistors are mostly used in fire alarms, refrigerators and ovens.
LDR( Light Dependent Resistors)
LDR (Light Dependent Resistors) is a light sensing device that changes its resistance as per the light intensity. It is also called as photoresistors. With the increase in light intensity, the resistance of LDR decreases.
Varistor
A varistor is a voltage-dependent resistor (VDR). In varistor, resistance is variable it depends upon the voltage applied. When voltage increases the resistance of the varistor decreases.
Flexible resistor
The flexible resistor is also called as the flex sensor. The resistance of a flexible resistor changes when it bends. This resistor is mostly used in the field of robotics.
How do resistors work?
Resistors function based on Ohm’s law, which states that the current passing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied and inversely proportional to the resistance.
In terms of mathematical representation, Ohm’s law takes the form:
V = I × R
Where:
V is the voltage across the resistor.
The letter ‘I’ represents the electric current passing through the resistor.
R is the resistance value in ohms.
When a voltage is applied to a resistor, a potential difference is created, and electrons encounter resistance as they flow through the material. This results in the dissipation of electrical energy in the form of heat.
Power in Resistors
Resistors are very useful semiconductor devices. According to circuits and their voltage consumption, resistors come in various powers such as 1.5Watt, 1Watt, 2Watt etc. The power of the resistor can be calculated by using the following formulas:
- Power = Voltage x Current {P = VI}
- Power = (Voltage)2 / Resistance {P = V2/R}
- Power = (Current)2x Resistance {P = I2 R}
Importance of Resistors in Electronic Circuits
Resistors are crucial components in electronic circuits for various reasons:
i. Current Limitation: One of the primary functions of resistors is to limit the amount of current flowing through specific parts of a circuit, protecting sensitive components from damage due to excessive current.
ii. Voltage Division: Electronics resistors are used in voltage dividers, allowing the distribution of voltage across different elements of a circuit.
iii. Biasing Transistors: Resistors are used in biasing transistors to set the operating point, ensuring proper amplification and functionality.
iv. Signal Conditioning: In signal processing, resistors are used for filtering, attenuation, and impedance matching to optimize signal quality.
v. Current Sensing: Resistors play a vital role in current sensing applications, such as overcurrent protection and feedback control in power supplies.
Applications of Resistors
Resistors have an extensive range of applications in numerous industries:
i. Electronics: Resistors are found in virtually all electronic devices, from smartphones and computers to televisions and gaming consoles.
ii. Telecommunications: In telecommunications, resistors are used in signal processing and line termination to reduce signal reflections.
iii. Power Generation and Distribution: Resistors are employed in power generation and distribution systems for load balancing and current control.
iv. Automotive: In automotive electronics, resistors are used in engine control units, airbag systems, and lighting controls.
v. Medical Devices: Medical equipment and devices often incorporate resistors for precision sensing and signal processing.
Power of Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Electric field charges and static electricity
Frequently Asked Questions
Ques 1. What is blower motor resistor?
Ans: The blower motor resistor is a crucial component in the HVAC system of a vehicle, responsible for regulating the speed of the blower motor and controlling the amount of air that is circulated throughout the cabin. Without a functioning blower motor resistor, the HVAC system may only be able to operate at a single speed or may not work at all, resulting in inadequate heating or cooling inside the vehicle.
Ques 2. What is pull up resistor?
Ans: A pull-up resistor is a component used in electronic circuits to ensure that a signal is in a known state when no other active device is driving it. In other words, a pull-up resistor is used to prevent a floating or undefined state in a signal line by providing a stable reference voltage when no other active device is actively driving the line.
The pull-up resistor is typically connected between the signal line and a positive voltage supply, such as VDD. This ensures that the signal line is pulled up to a high voltage level when not actively driven, creating a stable and defined state for the signal. The purpose of a pull-up resistor is to maintain a signal line in a known state when there is no active device driving it.
Ques 3. How to test the blower motor resistor?
Ans: To test a blower motor resistor, follow these steps:
- Ensure that the vehicle’s electrical system is turned off and the battery is disconnected to prevent any accidental electrical shocks or damage.
- Locate the blower motor resistor, which is typically found near the blower motor itself under the dashboard or in the engine compartment.
- Remove the blower motor resistor from its mounting location.
- Using a multimeter set to the resistance (ohm) setting, test the resistance between each of the blower motor resistor’s terminals.
- A reading of zero ohms or very low resistance indicates a short circuit, while a reading of infinite resistance indicates an open circuit.
Ques 4. What resistor to use with led?
Ans: The choice of the resistor to use with an LED depends on the specific LED’s forward voltage and the desired operating current. It is important to calculate the appropriate resistance value using Ohm’s law, which states that resistance (R) is equal to voltage (V) divided by current (I).
By determining the forward voltage of the LED and the desired current, you can calculate the suitable resistance value using the formula R = V/I. By using the appropriate resistor, you can ensure that the LED operates within its specified parameters and avoids any potential damage due to excessive current. Additionally, it is essential to consider the power rating of the resistor to ensure it can handle the power dissipated across it.
Ques 5. Which resistor is used to measure light intensity?
Ans: A light-dependent resistor is commonly used to measure light intensity. In the field of electronics, light intensity can be measured using a light-dependent resistor. The photoresistor, also known as a light-dependent resistor, is commonly used to measure light intensity.
Ques 6. Is resistor is active or passive?
A resistor is a passive component in an electric circuit. It does not actively generate or control the flow of electric current, but instead resists the flow of current that passes through it.
In electronic circuits, resistors play a crucial role in regulating the flow of electric current and protecting other components. They can limit the amount of current that flows through a circuit, divide the current between different components, reduce the voltage in a circuit, and provide heat or light.
Ques 7. How to determine resistor with colour codes?
The colour coding of resistors in an electronic component that is used to control the flow of electric current and has a specific value of resistance indicated by a series of colored bands. The colored bands on a resistor indicate the resistance value, tolerance, and sometimes the temperature coefficient of the component.
By carefully interpreting the colors on the resistor, one can determine its resistance value and use it effectively in electronic circuits. Additionally, the use of color coding allows for easy identification and differentiation of resistors, making it efficient for electronic circuit assembly and troubleshooting. Furthermore, the resistor color code system helps ensure consistency and accuracy in the selection and usage of resistors across various electronic devices and industries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, resistors are indispensable components in modern electronics, offering control over current flow and ensuring the proper functioning of electronic circuits. From fixed resistors to variable resistors and specialized thermistors, these tiny components play a significant role in our daily lives.
Whether you’re building a simple hobby project or working on cutting-edge technology, a solid understanding of resistors is essential. We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights into the world of resistors and their diverse applications. So, the next time you power up your electronic device, remember the critical role played by these unassuming yet indispensable components.
